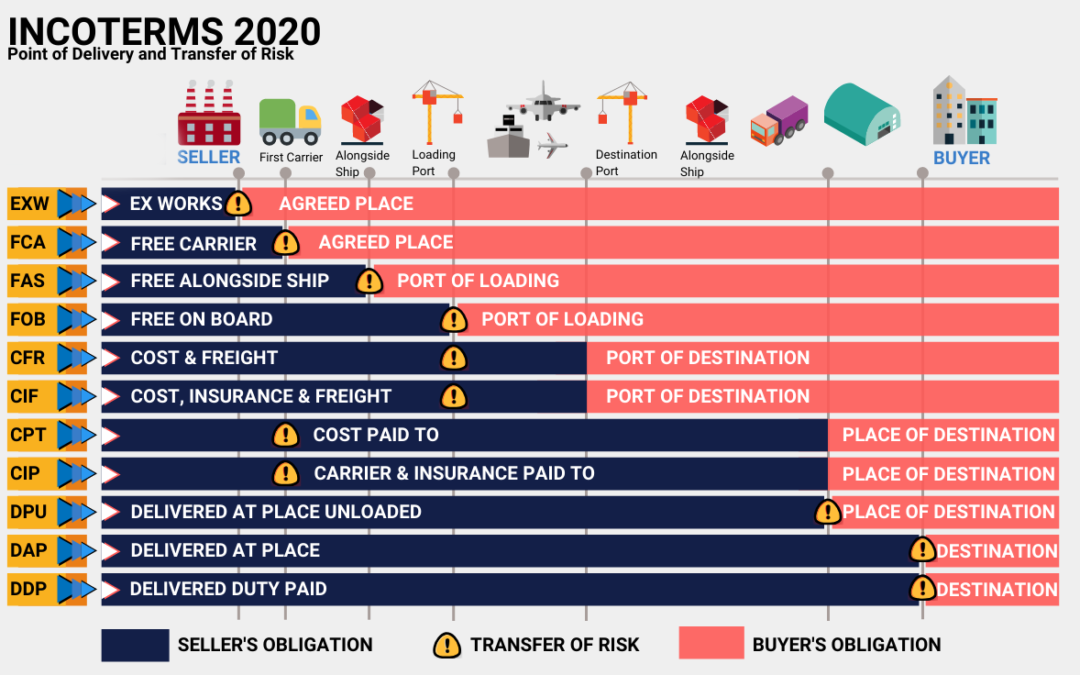
What are Incoterms?
Short for “International Commercial Terms,” the Incoterms are a set of globally recognized trade rules organized into 11 abbreviated terms. First published in Paris in 1936, by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), the Incoterms rules provide:
- Uniform interpretation of common contract clauses primarily found in export and import transactions
- Illustration of the timing and division of costs and risks between buyers and sellers
- Instructions to carriers, forwarders, customs brokers, banks, and other financial institutions involved in shipping goods
The Incoterms rules are not mandatory. They are not laws enacted by governments, but rather, guidelines agreed to by parties to a contract. Ultimately, it’s up to the buyer and the seller to agree to each party’s responsibilities, as well as the cost and risk of a shipment before it takes place.
E terms
F terms
C terms
D terms